In a world increasingly reliant on a steady flow of electricity, ensuring the consistent performance of electric generators is paramount. From powering industrial facilities to providing backup during outages, electric generators play a vital role across various sectors. A key aspect of this reliability lies in meticulous Electric Generator Maintenance.
Understanding the Importance of Electric Generator Maintenance
Just like any complex machinery, electric generators require regular upkeep to function optimally and have a long lifespan. Neglecting maintenance can lead to decreased efficiency, unexpected breakdowns, costly repairs, and even safety hazards.
Why is Electric Generator Maintenance Critical?
- Prevent Costly Downtime: Imagine a factory grinding to a halt due to a generator failure. Or a hospital facing a power outage with a malfunctioning backup generator. Regular maintenance significantly reduces the risk of such scenarios.
- Extend Generator Lifespan: A well-maintained generator can last for decades, providing a strong return on investment. Conversely, neglecting maintenance can lead to premature wear and tear, shortening the generator’s lifespan.
- Ensure Safety: Generators involve high voltage and moving parts. Proper maintenance mitigates the risk of electrical shocks, fires, and other accidents.
- Optimize Fuel Efficiency: A well-tuned generator runs more efficiently, consuming less fuel and reducing operating costs.
- Meet Environmental Regulations: Regular maintenance helps ensure generators operate within emissions standards, minimizing environmental impact.
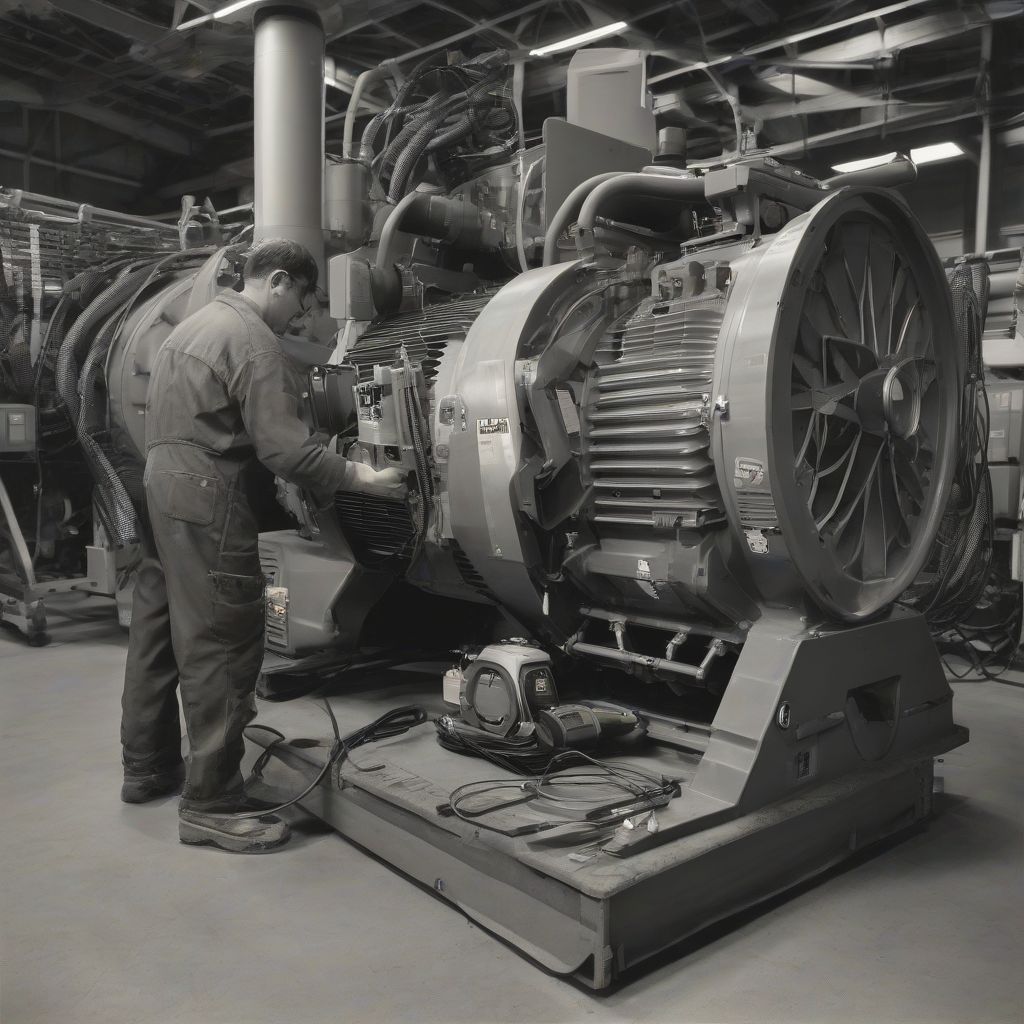 Generator Maintenance Technician
Generator Maintenance Technician
Key Aspects of Electric Generator Maintenance
Effective electric generator maintenance involves a multi-faceted approach, encompassing:
1. Routine Inspections
Regular visual checks are essential to identify potential issues before they escalate. This includes:
- Fluid Levels: Checking oil, coolant, and fuel levels.
- Battery Condition: Inspecting the battery for corrosion and ensuring it’s charged.
- Belts and Hoses: Looking for cracks, wear, and proper tension.
- Connections: Tightening loose connections and checking for signs of overheating.
2. Scheduled Maintenance
Depending on the generator’s size, type, and usage, scheduled maintenance might be recommended monthly, quarterly, or annually. This typically includes:
- Oil and Filter Changes: Vital for engine lubrication and longevity.
- Fuel System Inspection: Checking for leaks, clogs, and ensuring proper fuel flow.
- Cooling System Flush: Removing contaminants and maintaining optimal operating temperature.
- Spark Plug Replacement: Crucial for efficient combustion.
3. Load Bank Testing
Load bank testing simulates real-world operating conditions, allowing technicians to assess the generator’s performance under load. This helps identify:
- Output Capacity: Ensuring the generator can handle its intended load.
- Voltage and Frequency Regulation: Verifying stable power delivery.
- Transient Response: Evaluating the generator’s ability to handle sudden load changes.
4. Emergency Preparedness
Having a plan in place for potential generator issues is essential:
- Contact Information: Keep readily available the contact details of qualified generator technicians.
- Spare Parts Inventory: Maintaining a stock of essential parts can expedite repairs.
- Emergency Power Off Procedures: Ensure personnel are trained on how to safely shut down the generator in an emergency.
Addressing Common Electric Generator Maintenance Questions
How Often Should I Service My Generator?
The recommended service intervals vary depending on several factors, including:
- Generator Type: Diesel, natural gas, and propane generators have different maintenance requirements.
- Usage Frequency: A generator used frequently (e.g., in a hospital) will require more frequent maintenance than one used only for backup power.
- Operating Environment: Generators operating in harsh environments (e.g., extreme temperatures, dusty conditions) may need more frequent service.
Consulting the manufacturer’s recommendations and seeking guidance from qualified technicians is crucial to establishing an appropriate maintenance schedule.
What Are Common Signs of Generator Problems?
Being vigilant for warning signs can prevent major issues. These signs might include:
- Unusual Noises: Excessive vibration, knocking, or grinding sounds.
- Fluid Leaks: Oil, coolant, or fuel leaks around the generator.
- Exhaust Smoke: Black, white, or blue smoke can indicate different problems.
- Overheating: The generator running hotter than usual.
- Fluctuating Voltage: Lights flickering or appliances not working correctly.
The Role of Technology in Electric Generator Maintenance
Advancements in technology have revolutionized electric generator maintenance:
- Remote Monitoring: Sensors and connectivity allow for real-time data collection on generator performance, enabling proactive maintenance and remote diagnostics.
- Predictive Analytics: Data analysis can anticipate potential issues before they occur, allowing for scheduled maintenance and preventing costly downtime.
- Automated Reporting: Streamlining maintenance logs, reports, and regulatory compliance documentation.
Conclusion
In an era reliant on reliable power supply, electric generator maintenance is not just an option, it’s a necessity. By adhering to recommended maintenance schedules, being proactive in identifying potential issues, and embracing technological advancements, we can ensure these critical power sources remain operational when we need them most. Remember, an investment in electric generator maintenance is an investment in peace of mind and uninterrupted operations.